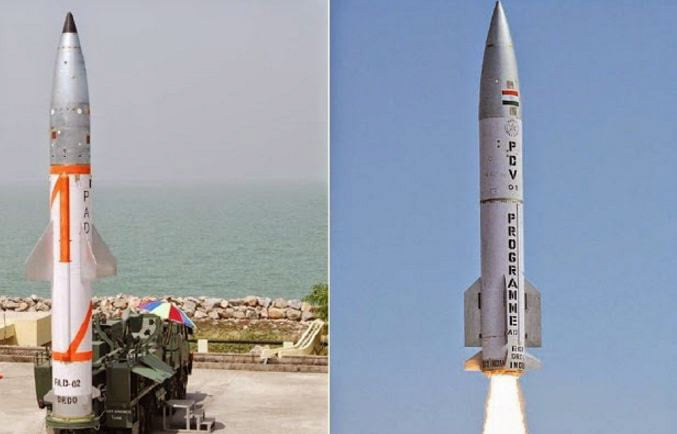
On September 23, India conducted a successful test of its Prithvi Defense Vehicle (PDV), an exo-atmospheric interceptor missile which is designed to engage medium-range ballistic missiles (MRBMs) at an altitude of approximately 66 km.
India’s Defense Research and Development Organization (DRDO) did not state the test’s objectives, but it likely focused on testing the missile’s intercept ability and not actually performing a kinetic intercept. The PDV receives guidance information from a radar-based detection and tracking system and navigates using an Inertial Navigation System (INS). The missile ejects its heat shield and engages its infrared seeker dome once it exits the atmosphere. DRDO reported that the missile executed this sequence as expected and successfully “engaged” the target.