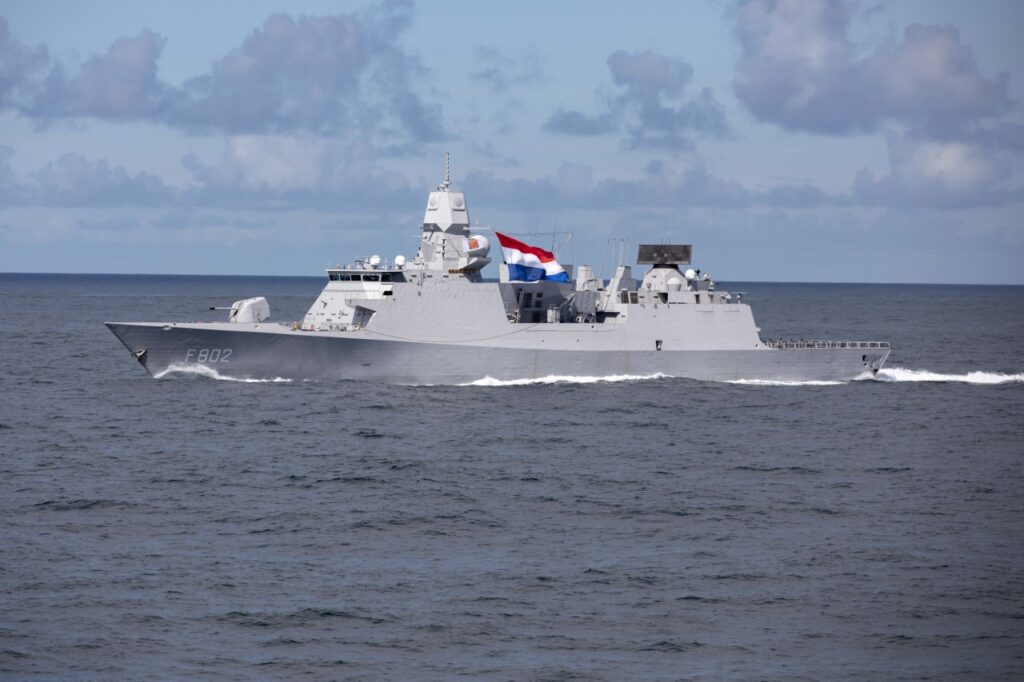
The U.S. Navy’s Arleigh Burke-class guided-missile destroyer USS Paul Ignatius destroyed a ballistic missile in close cooperation with Dutch frigate De Zeven Provinciën during the At Sea Demonstration/Formidable Shield 2021.
According to a story release issued by the Royal Netherlands Navy, Dutch frigate De Zeven Provinciën detected and tracked ballistic missile with Thales-made SMART-L radar and relayed the target information to USS Paul Ignatius. The Arleigh Burke-class destroyer intercepts the ballistic missile with SM-3 surface-to-air missile with the remote assistance of De Zeven Provinciën.

“Using the new SMART-L Multi-Mission/Naval radar, the Netherlands becomes the only European country that can simultaneously scan the airspace beyond the atmosphere and space up to 2,000 kilometers for air threats, such as (ballistic) missiles.
Following an aerial warning, the new SMART-L Multi-Mission/Naval radar detects ballistic missiles up to 2,000 kilometers away. The ship can then report this to allies, such as the Americans.
In addition to remote detection, the new SMART-L simultaneously ‘sees’ threats in the airspace. De Zeven Provinciën can protect a maritime squadron against anti-ship missiles fired from a distance. To defend against missiles outside the atmosphere, the Navy needs the Americans. They successfully destroyed a 14,000 km/h space-flying ballistic missile. That happened with an interceptor missile fired from the USS Paul Ignatius but based on the information provided by the SMART-L. The Netherlands itself does not have such missiles, which is why a partner took out the ‘enemy’ projectile.” said in the statement.
Naval Post considers this event is a critical milestone in the U.S.- Europe cooperation in defending against incoming ballistic missiles. SMART-L’s capability to detect ballistic missiles and Dutch De Zeven-class frigates’ ability to relay information continuously to Arleigh Burke-class destroyers is a new level of cooperation. Because ballistic missiles cruise really fast (in this event, the intercepted missile’s speed was 14.000 km/h), engaging BMs with information based on another ship’s sensor is a successful application of network-centric warfare application. In addition to the successful cooperation of NATO countries, this capability will relieve the U.S. about out of atmosphere surveillance issues.
SMART-L MM:
SMART-L is a 3D multibeam radar designed to provide long-range air & surface surveillance and target designation. A fully digitally controlled Active Electronically Scanned Array (AESA) radar. The applied high-end techniques result in radar with an unrivalled long-range performance of 2000 km. Within this enormous range, it detects a wide spectrum of targets: air-breathing targets, stealth targets and ballistic missiles. It can be installed on land-based locations, on the sea and is also available as Deployable Air Defence Radar.
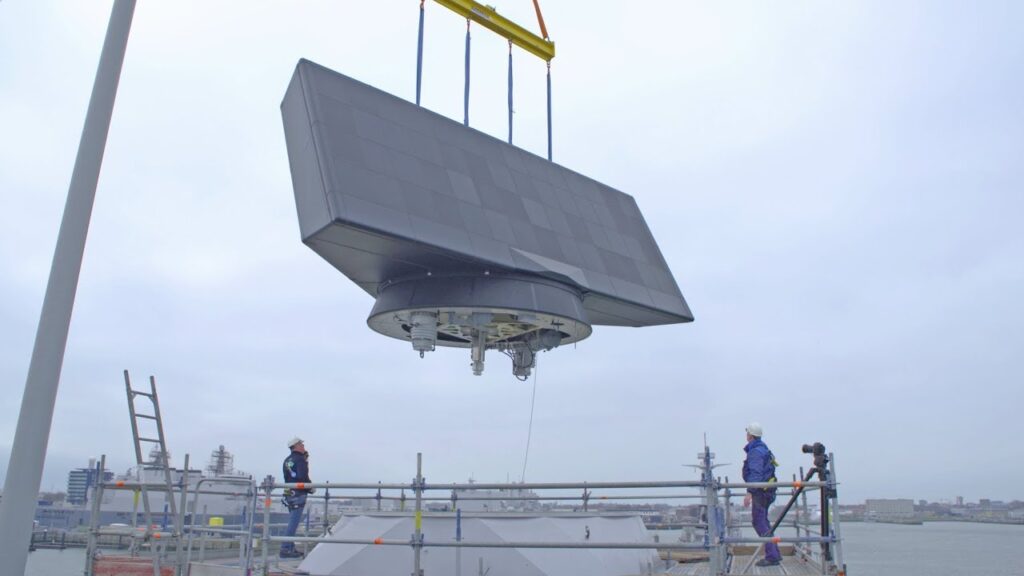

SMART-L MM independently finds Ballistic Missile type targets. Following fast track initiation, the ballistic target track is maintained up to the zenith. Ballistic Missile detection range is improved significantly by applying forward/backwards scanning and staring modes which provide increased observation time. The digitally controlled AESA type of radar, applying GaN transmitter and Dual Axis Multibeam receiver technology, is capable of detecting air and space objects including stealth, short up to long-range ballistic missiles and space objects.
In traditional radar systems, the functionality remains unchanged through its lifespan. However, SMART-L MM is an AESA programmable radar that is characterized by full flexibility. Additional capabilities can be introduced during a lifetime according to customer needs. This makes the radar future proof in case of evolving requirements.
SMART-L is operational on the Netherlands’, Danish and German air defence frigates and the Korean Landing Platform Dock. SMART-L’s derivative, S1850M, is operational on the Royal Navy’s Type 45 vessels and the French and Italian Horizon class destroyers. It is under contract for the new British Queen Elizabeth class aircraft carriers.
Check out Naval Library App to find out the specifications of SMART-L MM radars.