It is regarded as an essential and distinguished capability for a naval power to have the ability to attack long-distance strategic targets located in the depths of the land. Until 2015, it was thought that only the USA and Britain had this capability since they had Tomahawk cruise missiles. However, the United States and the United Kingdom are no longer the only nations with long-range cruise-missile engaging capability.
On October 7, 2015, the Russian Gepard-class frigate Dagestan and three small Buyan-class corvettes sailing in the Caspian Sea launched twenty-six Kalibr cruise missiles from the Vertical Launch Systems. The nine-meter-long cruise missiles flew up nine hundred miles over Iranian and Iraqi territory before slamming into targets into eleven targets in Syria, hitting a mix of ISIS fighters and Free Syrian Army rebels.
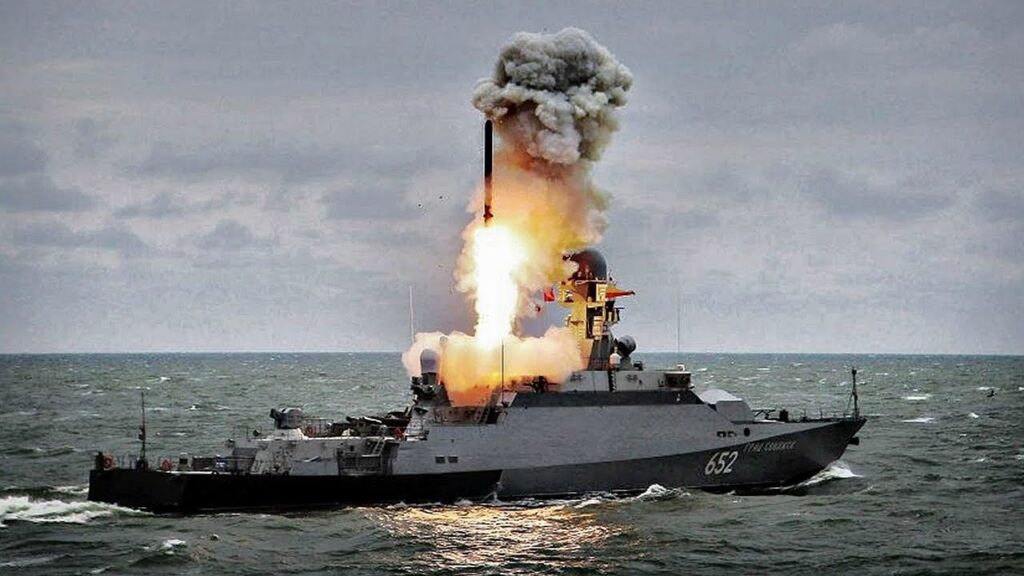

Kalibr missiles are currently deployed on Russian Navy Kilo-class submarines and more modern types, including the Akula, Lada, and Yasen classes. They are also deployed on frigates and corvettes—but so far have not been fitted on larger vessels, though such upgrades may eventually take place. While a Russian Gepard-class frigate is armed with only eight Kalibr missiles, a missile-armed destroyer would be able to carry dozens.
There are well over a dozen different variants in the Kalibr missile family, varying in launch platform, range, target profile, and speed, varying in length from six to nine meters, but all packing a 990-pound warhead or a nuclear payload. The land-attack variants, the 3M14T and 3M14K (NATO designation SS-N-30A) appear to lack the boost to Mach 3 on terminal approach. In compensation, the inertia-guided missiles have a range of between one thousand and 1,500 km. Guidance is ins, GPS, and digital scene matching area correlation (DSMAC), whereby images are taken during the flight by an onboard camera for comparison with stored ones. The Russian Navy has been planning to upgrade 3M14 “Kalibr” cruise missile with a longer-range “Kalibr-M” variant with a maximum firing range of more than 4,500 km.
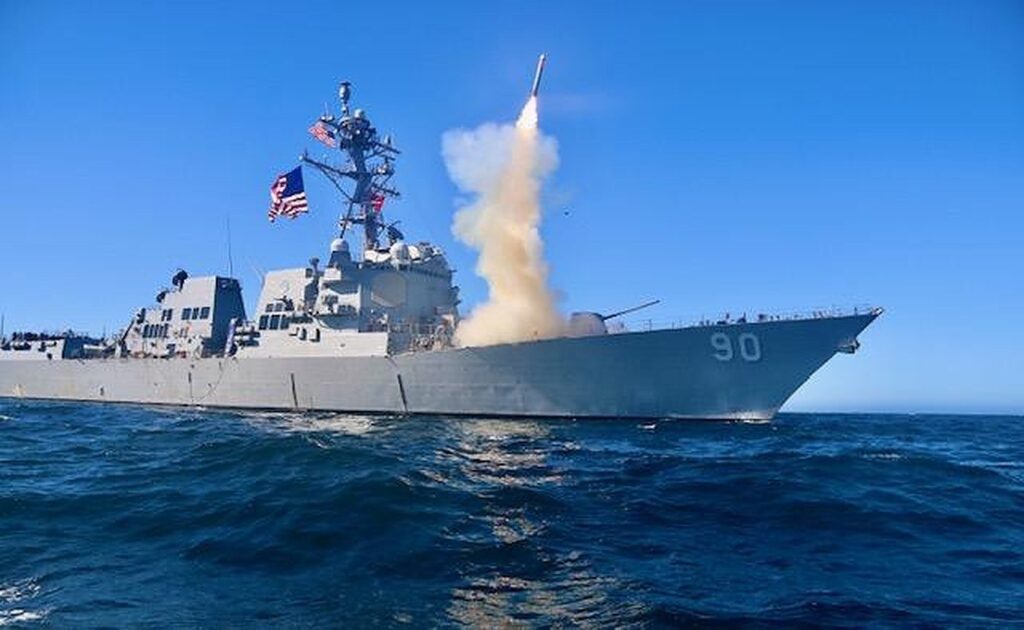
The Tomahawk (Land Attack Missile (TLAM) is a long-range, all-weather, subsonic cruise missile primarily used by the United States Navy and Royal Navy. Tomahawk cruise missile is capable of navigation by an inertial navigation system, GPS enabled precision strike, flies at very low altitude, and reprogrammable during flight to change target.
Guidance is GPS, Ins, terrain contour matching (TERCOM) navigation. This system compares the terrain underneath the cruise missile with mapping data stored inside the missile to detect deviations from its nominal trajectory.15 alternative pre-programmed targets can be held before flight or acceptance of a new target in-flight, delay and loiter option, battle damage assessment via two-way data link.
Tomahawk missile can take reconnaissance pictures after reaching a designated area and send them to the HQ via SATCOM and wait for their instructions. It can be loitered until the target is ‘clear to engage.’ With DSMAC (Digital Scene Mapping), a picture of a discrete target can be uploaded in a confined region and have Tomahawks specifically find and hunt them down.
With the modification Block V, Tomahawk has increased capabilities, which integrate new seeker, hitting the surface targets, more than 1000 miles range, greater penetrating power, less susceptible to jamming of its seeker and communication and navigation striking the target under the GPS taken down conditions.

Kalibr vs Tomahawk
The Kalibr suite was designed to compare favourably with Washington’s prolific but ageing Tomahawk cruise missiles. Whereas the original Kalibr 3M14 traded performance blows with the Tomahawk’s Block IV revision in what amounts to an approximate draw tilted slightly in Kalibr’s favour, Kalibr-M drastically outranges its US counterpart at 4,500 against 1,700 kilometres. The most significant advantage of the 3M14T and its family is that they can be fired from a wider variety of smaller ships than the American ones that usually carry the Tomahawk, making it easier to deploy. It is also being developed to fire from fixed land bases, vehicles, and aircraft.
Kalibr may not have some of the advanced loitering and interactive data link capabilities of the current Tomahawk, but that might well make it cheaper to mass-produce (in addition to parts commonality with family variants).
Tomahawk likely outclasses Kalibr is ECM capability. While Tomahawk’s IV block revision included electronic counter-countermeasures, the Kalibr family is relatively susceptible to jamming techniques. With the modification, Block V Tomahawk has improved its capabilities. Its networking capabilities are beyond that of most operational cruise missiles by a long margin.

Conclusion
It is impossible to make a complete comparison between two missiles with limited knowledge about KALIBR cruise missiles at this stage. The Tomahawk has over 30 years of proven combat effectiveness, while the Kalibir only appeared in 2012. The Tomahawk has been regularly upgraded and improved and renown for its accuracy, but Russia does not make public the accuracy or reliability of the Kalibr missiles it has fired. Anyhow Russian Navy has gained a strategic capability with Kalibr cruise missiles.
Check out Naval Library App to find out the specifications of Tomahawk and Kalibr missiles.